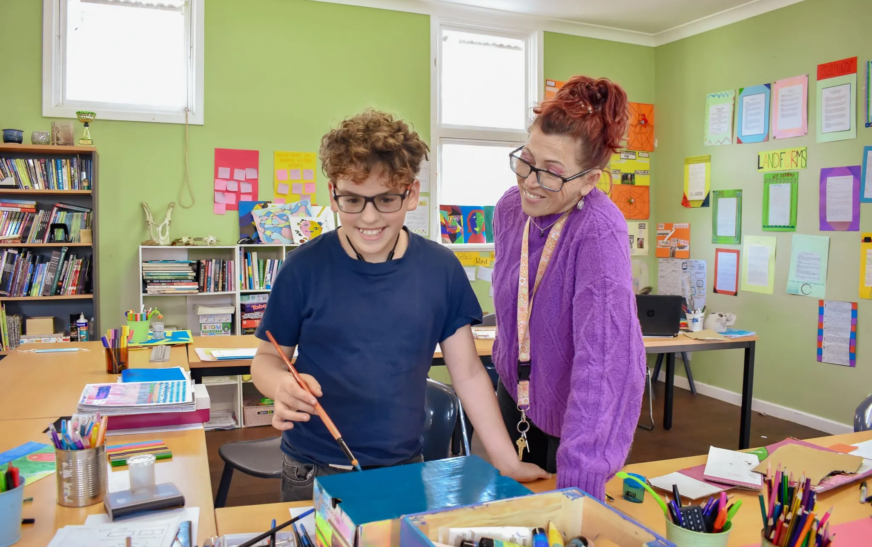
Nurturing student well-being is increasingly recognised as a critical component of academic success and personal development. Beyond traditional teaching methods, schools and educators are adopting strategies to support the holistic needs of students, addressing emotional, social, and mental health aspects.
Understanding Student Well-Being
Student well-being includes emotional health, social connections, and physical wellness. A holistic approach integrates these elements, recognising that students thrive when their overall well-being is supported.
Emotional Health
Emotional health involves the ability to manage and express emotions in a healthy way. It includes building resilience, coping with stress, and fostering a positive self-image. Students who feel emotionally supported are more likely to engage in their learning and exhibit better academic and behavioural outcomes.
Social Connections
Strong social connections are crucial for students’ well-being. Positive relationships with peers, teachers, and family members contribute to a sense of belonging and support. Social skills development, empathy, and effective communication are key components of a nurturing educational environment.
Physical Wellness
Physical wellness affects overall well-being and academic performance. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep are essential for maintaining energy levels and cognitive function. Schools play a significant role in promoting healthy lifestyle choices and providing resources for physical health.

Implementing Well-Being Programs
Effective well-being programs are designed to address the diverse needs of students and create a supportive learning environment. Here are some key strategies for implementing such programs:
1. Creating a Supportive School Culture
A positive school culture is foundational for student well-being. Schools should foster an environment where students feel safe, respected, and valued. This involves promoting inclusivity, celebrating diversity, and addressing bullying or discrimination. A supportive culture encourages students to seek help when needed and builds a sense of community.
2. Providing Access to Counselling and Mental Health Services
Access to professional counselling and mental health services is crucial for addressing students’ emotional and psychological needs. Schools should offer on-site counselling services or establish partnerships with external providers. Early intervention and support for mental health issues can prevent more severe problems and help students develop coping strategies.
3. Incorporating Social-Emotional Learning (SEL)
Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) programs teach students essential skills for managing emotions, setting goals, and building positive relationships. SEL can be integrated into the curriculum through specific lessons or activities and is most effective when embedded into everyday school life. Training teachers in SEL techniques enhances their ability to support students effectively.
4. Promoting Physical Health
Schools can promote physical health by offering nutritious meal options, encouraging regular physical activity, and educating students about healthy lifestyle choices. Physical education programs should be engaging and inclusive, catering to various interests and abilities. Additionally, providing resources and support for students with specific health needs is important for overall well-being.
5. Engaging Families and Communities
Family and community involvement is vital in nurturing student well-being. Schools should actively engage parents and caregivers through regular communication, workshops, and involvement in school activities. Collaborating with community organisations can provide additional resources and support for students and their families.

Monitoring and Evaluating Well-Being Programs
To ensure the effectiveness of well-being programs, schools should regularly monitor and evaluate their impact. This involves collecting feedback from students, parents, and staff, as well as analysing data on student outcomes and well-being indicators. Continuous evaluation helps identify areas for improvement and adjust programs to better meet the needs of students.
1. Collecting Feedback
Gathering feedback from students, parents, and teachers provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of well-being initiatives. Surveys, focus groups, and informal discussions can help identify strengths and areas for improvement. Actively involving students in the evaluation process empowers them and ensures their voices are heard.
2. Analysing Data
Data analysis is essential for understanding the impact of well-being programs. Schools should track key indicators such as attendance, academic performance, and behavioural issues. Comparing these indicators before and after implementing well-being initiatives can provide evidence of their effectiveness and guide future decisions.
3. Adjusting Programs
Based on feedback and data analysis, schools should be prepared to adjust their well-being programs as needed. Flexibility and responsiveness to emerging needs or challenges are crucial for maintaining the relevance and effectiveness of initiatives. Regular updates and improvements help ensure that programs continue to support student well-being effectively.
Conclusion
Effectively nurturing student well-being requires a comprehensive and proactive approach. By creating a supportive school culture, providing access to mental health services, incorporating social-emotional learning, promoting physical health, and engaging families and communities, schools can foster an environment where students thrive academically and personally. Continuous monitoring and evaluation ensure that well-being programs remain effective and responsive to students’ needs. As exemplified by Fairbridge Education, prioritising student well-being leads to positive outcomes and supports the holistic development of students.