Australia’s food manufacturing sector is facing a critical juncture as escalating costs threaten to disrupt the industry and influence supermarket practices. This blog post delves into the current challenges faced by Australian food manufacturers and the potential implications for the retail sector.
The Financial Strain on Food Manufacturers
Australia’s food manufacturing industry is grappling with a surge in operational costs, driven by various factors including raw material price hikes, energy expenses, and supply chain disruptions. According to industry experts, the costs associated with producing and distributing food products have increased significantly, placing immense pressure on manufacturers to maintain profitability.
These rising costs are not only affecting manufacturers but also reverberating throughout the supply chain. The increased financial burden has led many companies to reconsider their production strategies and explore cost-saving measures. As a result, the industry is facing a pivotal moment where strategic decisions will shape its future.
Impact on Supermarket Supply Chains
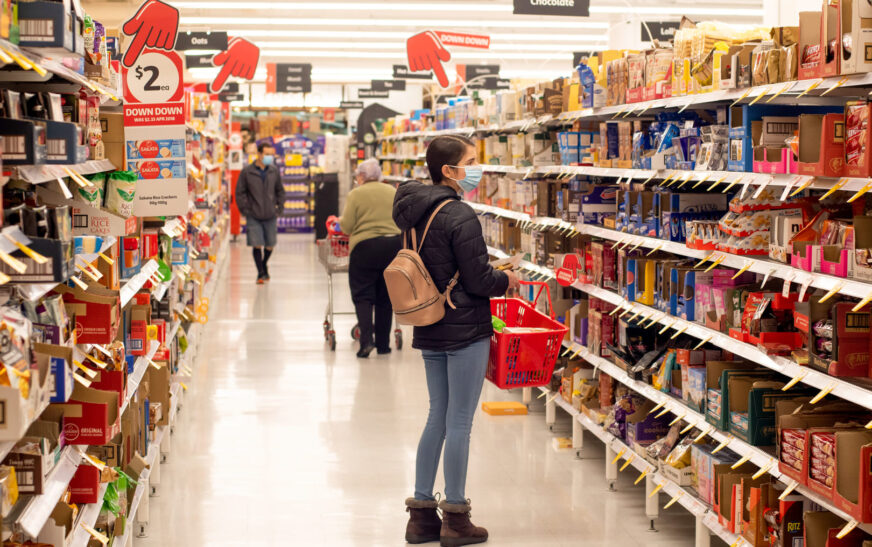
Supermarkets, as key stakeholders in the food supply chain, are directly impacted by the rising costs within the manufacturing sector. With the pressure to keep retail prices competitive, supermarkets are confronted with a challenging decision: absorb the increased costs or pass them on to consumers.
In recent months, there has been a noticeable shift towards sourcing more imported food products as a cost-cutting measure. Imported goods, often priced lower due to different production costs in other countries, provide an attractive alternative for supermarkets aiming to maintain price competitiveness. This trend raises concerns about the future of locally produced food and its share in supermarket shelves.
The Shift Towards Imports
The rising costs faced by Australian food manufacturers have made imported products more appealing for supermarkets. With price pressures mounting, the shift towards importing food products is becoming more pronounced. This change is driven by the need to offer consumers affordable options while managing the financial strain on retail operations.
While importing food products may alleviate some immediate cost pressures, it also brings about several implications. The increased reliance on imports can potentially impact the local food manufacturing sector, leading to reduced demand for domestic products. This, in turn, may have consequences for local employment, regional economies, and the overall sustainability of the food industry.
Potential Consequences for Local Food Production
The growing inclination towards imported food products raises concerns about the future of Australia’s local food manufacturing industry. The shift may result in decreased demand for domestically produced goods, affecting local manufacturers’ revenues and potentially leading to job losses within the sector.
Moreover, the reliance on imports could have broader implications for food security and supply chain resilience. By increasing dependence on international sources, the industry may become more vulnerable to global supply chain disruptions, trade policy changes, and geopolitical uncertainties.
Addressing the Challenges
To address the challenges posed by rising costs and the shift towards imports, stakeholders in the food manufacturing and retail sectors need to collaborate on strategic solutions. Initiatives to enhance operational efficiency, reduce production costs, and strengthen local supply chains can play a crucial role in supporting the industry.
Investment in technological advancements, innovation in production processes, and diversification of sourcing strategies can contribute to mitigating the impact of rising costs. Additionally, government support and policy measures aimed at promoting local food production and reducing regulatory burdens can provide valuable assistance to the industry.
Conclusion
Australia’s food manufacturing industry is navigating a complex landscape marked by rising costs and a growing inclination towards imported products. The impact on supermarkets and the broader food supply chain highlights the need for strategic responses to address these challenges. By fostering collaboration, embracing innovation, and supporting local production, stakeholders can work towards ensuring a sustainable and resilient food manufacturing sector for the future.
As the industry evolves, staying informed about these developments will be crucial for all stakeholders involved in the food supply chain, from manufacturers to retailers and consumers.